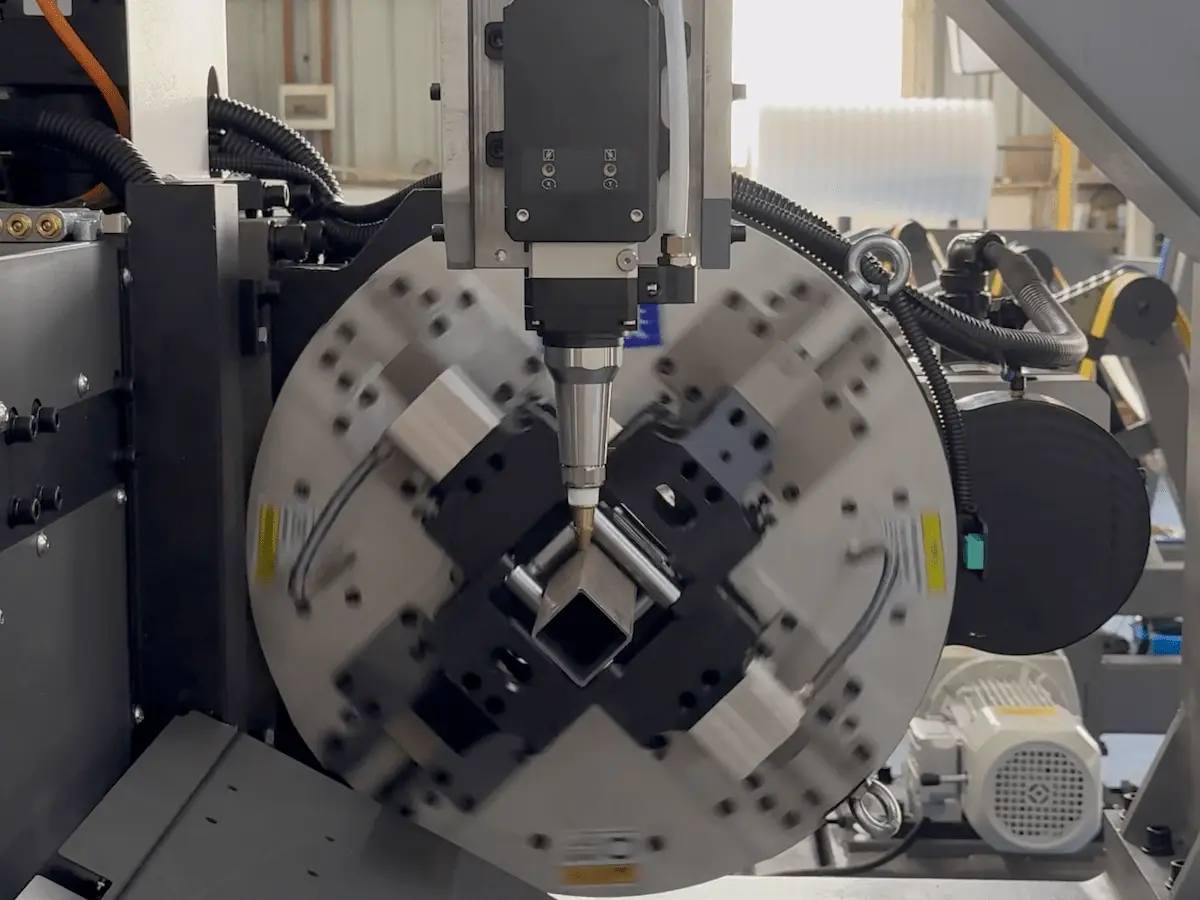
In the intricate world of medical device manufacturing, precision isn’t just a goal—it’s a necessity for ensuring patient safety and device efficacy. As an engineer at Longxin Laser with extensive experience in developing cutting systems, I’ve seen how laser tube cutting technology enables the creation of components that traditional methods simply can’t match. From stents that navigate delicate vascular pathways to hypotubes guiding minimally invasive procedures, this approach delivers the accuracy required for life-saving tools. With the medical industry demanding ever-smaller, more complex parts, understanding the precision applications of laser tube cutting reveals why it’s becoming indispensable for factories aiming to innovate and comply with stringent regulations.
The Critical Need for Precision in Medical Devices
Medical devices often operate in environments where even a micron of error can lead to complications, such as in cardiovascular interventions or orthopedic implants. Precision ensures biocompatibility, reduces tissue trauma, and enhances functionality—think of a stent that must expand uniformly without sharp edges that could cause inflammation. Laser tube cutting addresses these demands by allowing cuts with tolerances down to 0.01 mm, far surpassing mechanical methods that risk burrs or distortions. This level of control is essential in a field where regulatory bodies like the FDA emphasize defect-free production, making it a smart choice for manufacturers looking to minimize recalls and boost reliability.
How Laser Tube Cutting Delivers Unmatched Accuracy
At its core, laser tube cutting uses focused beams—often from fiber or femtosecond lasers—to vaporize material without physical contact, preserving the tube’s integrity. Fiber lasers excel in metal tubes like stainless steel or nitinol, common in medical applications, while femtosecond pulses handle polymers with minimal thermal damage. This non-contact process eliminates tool wear and allows for intricate features like slots or holes in a single pass.
- Minimal Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): Unlike traditional cutting, lasers limit heat spread, preventing material weakening that’s critical for shape-memory alloys in stents.
- Burr-Free Edges: The clean cuts reduce post-processing, saving time and ensuring smooth surfaces that won’t irritate biological tissues.
- Complex Geometries: CNC integration enables 3D patterns on curved tubes, ideal for custom devices tailored to patient anatomy.
In my work at Longxin Laser, we’ve optimized these systems to handle diameters as small as 0.5 mm, proving essential for the precision-driven medical sector.
Key Applications in Medical Devices
Laser tube cutting shines in producing components for a range of medical tools, where accuracy directly impacts performance.
- Stents and Vascular Devices: For coronary stents, lasers cut intricate mesh patterns from nitinol tubes, allowing controlled expansion. Research in the Journal of Materials Processing Technology shows how parameter adjustments like pulse frequency achieve surface roughness below 0.5 μm, vital for thrombosis prevention.
- Hypotubes for Catheters: These thin-walled tubes require precise slots for flexibility; laser cutting ensures consistent results without compromising strength, as used in guiding wires for endoscopy.
- Surgical Instruments: Precision cuts create ergonomic handles or blades from metal tubes, enabling minimally invasive surgery with tools that fit through tiny incisions.
- Implants and Prosthetics: Custom orthopedic implants benefit from laser-cut tubes that form lightweight, durable structures, improving patient mobility.
- Polymer Tubes for Drug Delivery: Ultrafast lasers process biocompatible polymers for tubing in infusion systems, offering clean holes for controlled release.
These applications highlight why laser technology is necessary—traditional sawing can’t handle the delicacy required, often leading to higher failure rates in clinical trials.
Performance Metrics: Laser vs. Traditional Methods
To underscore the advantages, here’s a comparison based on data from academic studies and industry reports, including insights from Procedia Manufacturing and MDPI journals:
| アスペクト | Laser Tube Cutting | Traditional Methods (e.g., EDM or Sawing) |
| Tolerance | ±0.01 mm | ±0.1 mm or more |
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | <0.5 μm | 1-5 μm |
| Processing Speed | Up to 50 mm/s for thin tubes | 5-20 mm/s |
| Heat-Affected Zone | Minimal (<50 μm) | Significant (>200 μm) |
| Material Waste | Low (kerf ~0.05 mm) | Higher due to wider cuts |
| Post-Processing Needed | Rarely | Extensive (deburring, polishing) |
These figures, drawn from research on nitinol processing, demonstrate how laser systems reduce costs by 20-30% through efficiency, making them a worthwhile upgrade for medical manufacturers.
Real-World Impact and Case Insights
The technology’s value is evident in practical scenarios. A study in Optics and Lasers in Engineering detailed a manufacturer using femtosecond lasers to cut NiTi tubes for self-expanding stents, achieving 40% faster production and zero defects in batches of 1,000 units. Similarly, in polymer applications, SPIE proceedings report on glass tube cutting for lab-on-a-chip devices, where ultrafast lasers enabled complex contours without cracking, advancing diagnostic tools.
At Longxin Laser, we’ve supported clients in similar projects, like optimizing cuts for hypotubes in interventional cardiology, resulting in quicker market entry and compliance with ISO 13485 standards. These examples show the necessity: in competitive medtech, precision laser cutting turns innovative designs into viable products, often shortening development cycles by months.
Overcoming Challenges and Looking Ahead
While laser tube cutting offers precision, challenges like initial setup costs ($150,000+) and material-specific parameter tuning exist. However, advancements in AI integration for real-time adjustments are mitigating these, as explored in Frontiers in Physics. Future trends point to hybrid systems combining lasers with robotics for fully automated lines, essential for scaling production amid growing demand for personalized medicine.
Why Precision Matters for Your Operations
Embracing laser tube cutting for medical devices isn’t about following trends—it’s about delivering reliable, high-performance components that save lives. As the industry evolves, this technology positions factories to meet rising standards and explore new markets.