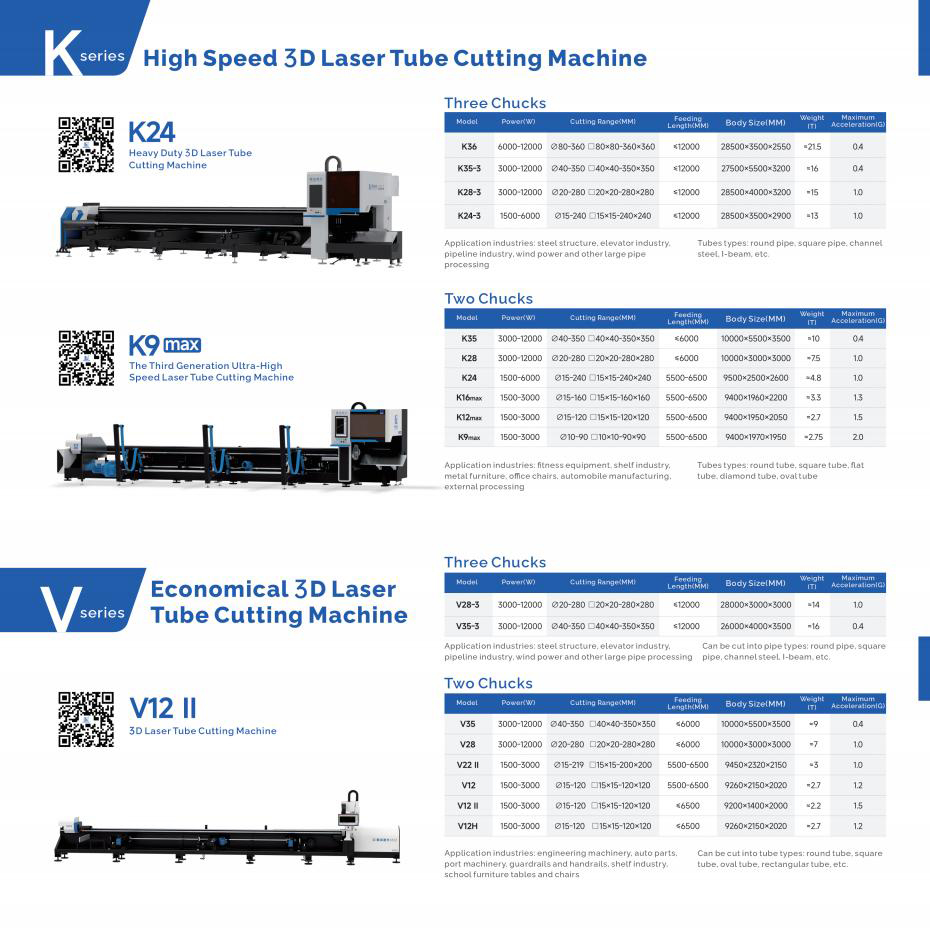
What is a Pipe Bender Machine?
A pipe bender machine is a specialized tool used for bending pipes and tubes into desired shapes and angles. These machines are essential in various industries, including plumbing, automotive, and construction, where precise bends are required to navigate obstacles or create complex piping systems.
How Does A Pipe Bender Machine Work?
A pipe bender machine operates by applying force to metal pipes or tubes to bend them into specific shapes and angles. The process typically involves several key steps:
Preparation: The operator selects the appropriate bending die based on the desired angle and radius, and the machine is activated.
Clamping: The pipe is securely clamped in place to prevent movement during the bending process.
Flattening: Initial pressure is applied to slightly flatten the pipe, creating a deformation zone that makes it easier to bend.
Bending: The machine exerts force on the pipe, causing it to curve around the bending die. This is controlled through a hydraulic system or electric motors, depending on the machine type.
Release: Once the desired bend is achieved, the pressure is released, and the clamp is opened, allowing the bent pipe to be removed.
What are the main types of pipe-bending machines?
The main types of pipe-bending machines can be categorized based on their operation and application. Here are the primary types:
Manual Pipe Benders:
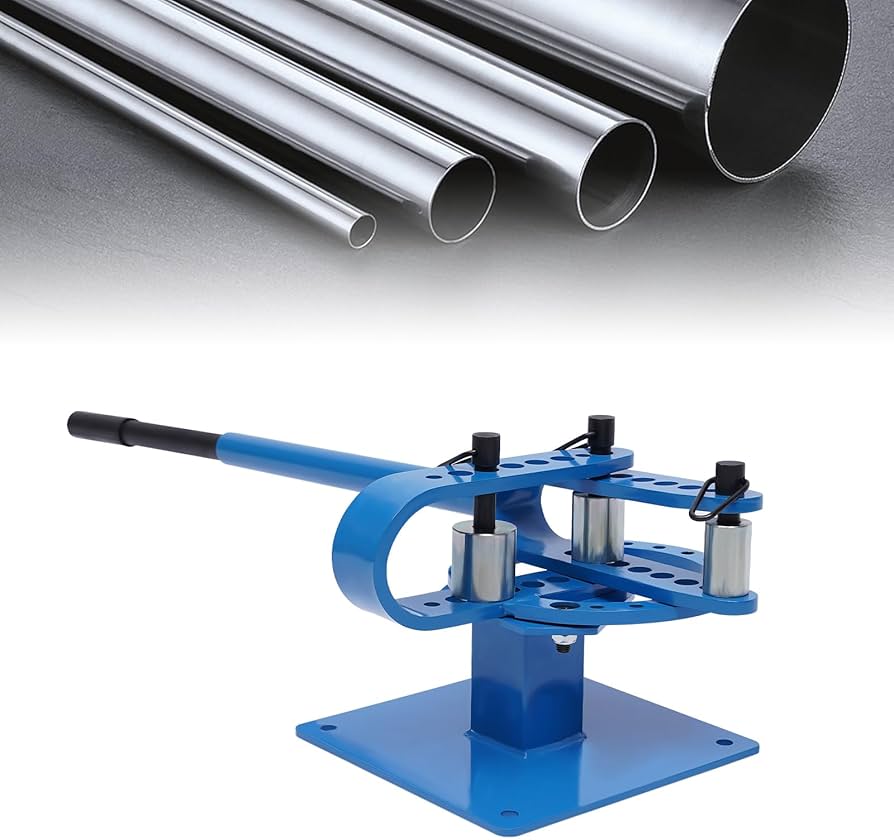

These are the simplest and most economical machines, operated by hand. They are suitable for small projects requiring basic bends.
Hydraulic Pipe Benders:
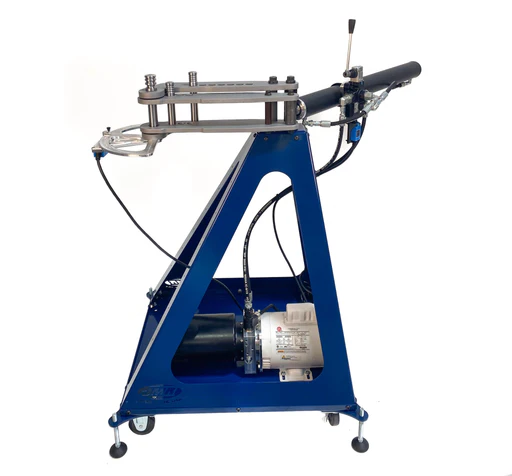

Utilizing hydraulic pressure, these machines can create precise bends in larger and thicker pipes. They are favored for their efficiency and ability to handle complex shapes.
Electric Pipe Benders:

These machines use electric power for operation, offering semi-automatic bending processes. They are ideal for medium-diameter pipes and more complex bends.
CNC Pipe Benders:

A CNC tube bending machine uses a servo motor to replace the hydraulic drive, allowing separate control of the carriage’s forward and backward movements, the rotation of the tilt angle, bending of the elbow, auxiliary feed and retract, as well as the lifting and lowering of the machine head. Although clamping, annealing, core feeding, and pushing are still performed by hydraulic drive, the CNC tube bending machine offers higher precision and efficiency.
Pneumatic Pipe Benders:
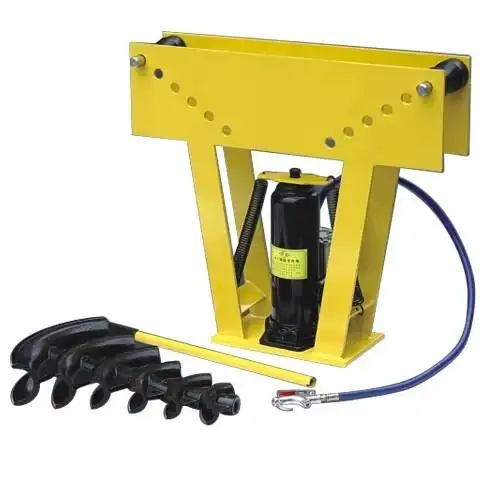

These operate using compressed air, offering advantages similar to hydraulic benders but often at a lower cost.
Roll Bending Machines:
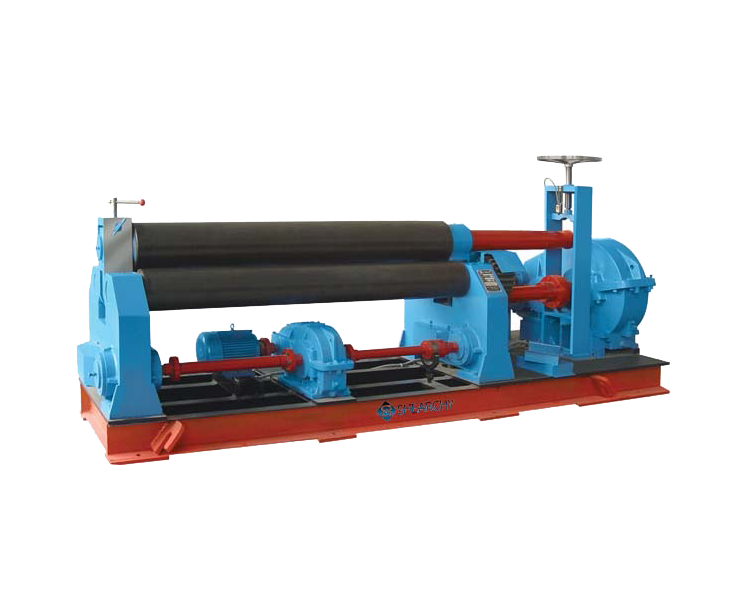

Designed for large-radius bends, these machines can process various profiles and are commonly used in construction and engineering applications.
Each type of pipe bending machine has its advantages and is suited for different applications, depending on factors like pipe material, diameter, and the complexity of the required bends
What are the applications of pipe-bending machines?
Automotive Industry: Pipe bending machines are widely used to manufacture components such as exhaust pipes, fuel lines, and cooling system ducts. They ensure the accuracy needed for vehicle performance and safety
Aerospace Industry: In aerospace, these machines produce critical components like fuel pipes and structural elements for aircraft and satellites. Precision is vital here to maintain safety standards
Construction: Pipe bending is crucial for creating air conditioning ducts, water supply lines, and structural supports. The machines enable the efficient production of complex shapes required in modern architecture
Oil and Gas: The industry relies on tube bending for pipelines that transport oil, gas, and other fluids. Bending machines facilitate the creation of complex layouts necessary for these systems
HVAC Systems: Benders are used to fabricate ductwork and piping systems that require specific bends to fit within building designs, enhancing efficiency in heating and cooling systems
Home Appliances: In manufacturing appliances like refrigerators, tube bending machines create cooling pipes that are essential for functionality
What types of Pipes can a pipe bender machine bend?
Steel Pipes: Commonly used in construction and manufacturing, steel pipes can be bent using hydraulic or mechanical benders, making them suitable for structural applications.
Stainless Steel Pipes: Known for their durability and resistance to corrosion, stainless steel pipes are often bent using cold or hot bending techniques, especially in industries requiring high material performance.
Aluminum Pipes: Lightweight and easy to work with, aluminum pipes are commonly bent in automotive and aerospace applications. They can be processed using various bending machines.
Copper Pipes: Frequently used in plumbing and refrigeration, copper pipes can be bent easily with manual or hydraulic benders, allowing for efficient installation around obstacles.
PVC Pipes: While typically not as common for traditional bending, specialized PVC pipe benders can create curves in plastic piping used in irrigation and drainage systems.
Carbon Steel Pipes: These are often used in oil and gas applications and can be bent with hydraulic machines to create complex shapes needed for piping systems.
Conduit Pipes: Used primarily for electrical wiring, conduit pipes can be bent using manual or electric pipe benders to navigate around structures without creating joints.
How to Choose the Right Pipe Bender Machine?
Evaluate Production Requirements
Determine the range of pipe diameters you need to work with
Consider that each pipe bender machine has its parameter limitations
Assess your production volume and frequency of use
Define Key Technical Parameters
a) Material Types to be Bent:
Steel pipes
Stainless steel pipes
Aluminum pipes
Copper pipes
PVC pipes
Carbon steel pipes
Conduit pipes
b) Pipe Specifications:
Cross-section type (round, square, angle iron)
Outer diameter
Wall thickness
Bending radius (measured at pipe center)
Consult with Manufacturers
Provide all specified parameters to the supplier
Get professional recommendations on suitable models
Compare different machine capabilities
Consider Machine Capabilities
Check maximum and minimum pipe sizes
Verify compatibility with your required materials
Ensure the bending radius meets your specifications
Confirm the machine can handle your pipe cross-sections
Additional Considerations
Machine type (manual, hydraulic, or CNC)
Space requirements
Operating requirements
Maintenance needs
How to use the pipe bender machine?
1. Preparation
Choose the appropriate tube bending machine model and mold based on the tube’s material, diameter, and bending requirements. Verify that the bending machine is in proper working condition. Clean the tube’s surface to remove any oil, rust, or other contaminants.
2. Tube Clamping
Accurately position the tube in the bending machine’s clamp, ensuring it is securely fastened and precisely aligned.
3. Parameter Settings
Configure the bending speed, force, and other parameters according to the tube specifications and required bending angle.
4. Bending Operation
Start the bending machine and proceed with the bending slowly, while closely monitoring the tube’s deformation. Adjust the feed speed during the process to prevent issues such as wrinkling or cracking.
5. Quality Inspection
Upon completion of the bending, inspect the angle, roundness, and surface quality to ensure they meet the specified standards. If any discrepancies are found, identify the cause and make necessary adjustments before re-bending.
6. Post-Processing
Clean and finish the tubes that meet the bending criteria as needed.
Common Tube Bending Machine Faults and Repair Methods
Fault 1: Inaccurate Bending Angle
Repair Methods:
– Verify the CNC program settings and correct the parameters if necessary.
– Check if the sensors are functioning properly; replace any damaged sensors.
– Inspect the mechanical transmission components for looseness or wear and tighten or replace parts as needed.
Fault 2: Abnormal Noise During Operation
Repair Methods:
– Check if any components are loose and tighten the relevant screws.
– Inspect the lubrication of transmission components and add or replace lubricant if needed.
– Ensure no foreign objects are obstructing the machine structure; clear any obstructions.
Fault 3: Hydraulic System Malfunction
Repair Methods:
– Check the hydraulic oil level and refill or replace it as necessary.
– Inspect the oil pipes for leaks and repair or replace them if found.
– Verify the operation of hydraulic valves and other components; repair or replace them if needed.
Fault 4: Display Screen or Control System Issues
Repair Methods:
– Ensure the electrical connections are secure; reseat any cables if necessary.
– Reset or restart the control system.
– If the issue persists, professional inspection or control board replacement may be required.
Fault 5: Wrinkles or Deformation in Bent Tubes
Repair Methods:
– Adjust the bending parameters, such as speed and pressure.
– Check the molds for wear or damage and repair or replace them as needed.
Safety Issues During Tube Bending Machine Operation
1. Operator Training
Ensure operators receive professional training and are familiar with the machine’s operation procedures and safety regulations.
2. Protective Devices
Inspect and ensure protective guards and covers are intact to prevent contact with moving parts.
3. Workpiece Securing
Ensure tubes or other workpieces are securely fastened to the bending machine to prevent them from coming loose during processing.
4. Operating Space
Keep the operating area clean and free of obstructions to avoid tripping or collisions during operation.
5. Emergency Stop Button
Make the location of the emergency stop button known for quick access in case of an abnormal situation.
6. Electrical Safety
Regularly inspect electrical wiring to prevent issues such as leakage or short circuits.
7. Mold Inspection
Regularly check and maintain molds to ensure they are free from damage or looseness, preventing accidents during use.
8. Noise Protection
When working in a high-noise environment for extended periods, use earplugs or other ear protection.
9. Prohibit Unauthorized Operations
Strictly follow operating procedures and avoid risky or non-compliant actions.
10. Equipment Maintenance
Regularly maintain and service the bending machine to promptly identify and address potential safety hazards.