Introduction: More Than Just a Name
What is the difference between a pipe cutter and a tube cutter?
Although these tools may appear similar at first glance, they are designed for fundamentally different materials: pipes and tubes. This distinction is not just semantic. Choosing the wrong cutter can result in poor fitment, material deformation, system failure, or unnecessary rework.
Whether in plumbing, construction, or manufacturing, understanding this difference is essential for selecting the correct tool and ensuring efficient, reliable results.
To fully understand the difference between pipe cutters and tube cutters, we must first examine the distinction between pipes and tubes themselves.
Pipes vs. Tubes: The Foundational Difference
The difference between pipe cutters and tube cutters originates from how pipes and tubes are defined, measured, and used in industry.
What Is a Pipe?
A pipe is primarily used to transport fluids or gases. In industrial and commercial applications, pipes are specified using:
- Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) or DN (Diamètre Nominal)
- Schedule (Sch 10, Sch 40, Sch 80, etc.)
It is important to understand that NPS is not a physical measurement. For example, a pipe labeled NPS 2 has an actual outside diameter (OD) of 2.375 inches, not 2 inches.
Key characteristics of pipes include:
- The outside diameter remains constant for a given NPS
- The schedule defines the wall thickness
- Higher schedules indicate thicker walls and smaller inside diameters
- Standardized OD allows compatibility with fittings regardless of schedule
This standardization makes pipes ideal for fluid transport systems, where interchangeability, pressure rating, and flow capacity are critical.
What Is a Tube?
A tube is commonly used in structural, mechanical, and precision applications where exact dimensions are required.
Tubes are specified by:
- Exact outside diameter (OD)
- Exact wall thickness
Unlike pipes, tubes:
- Do not use nominal sizing
- Are measured by their actual physical dimensions
- Are manufactured with tighter dimensional tolerances
This precision is essential in applications such as metal fabrication, automotive manufacturing, furniture production, and mechanical engineering.
Pipe Cutter vs. Tube Cutter: Key Tool Differences
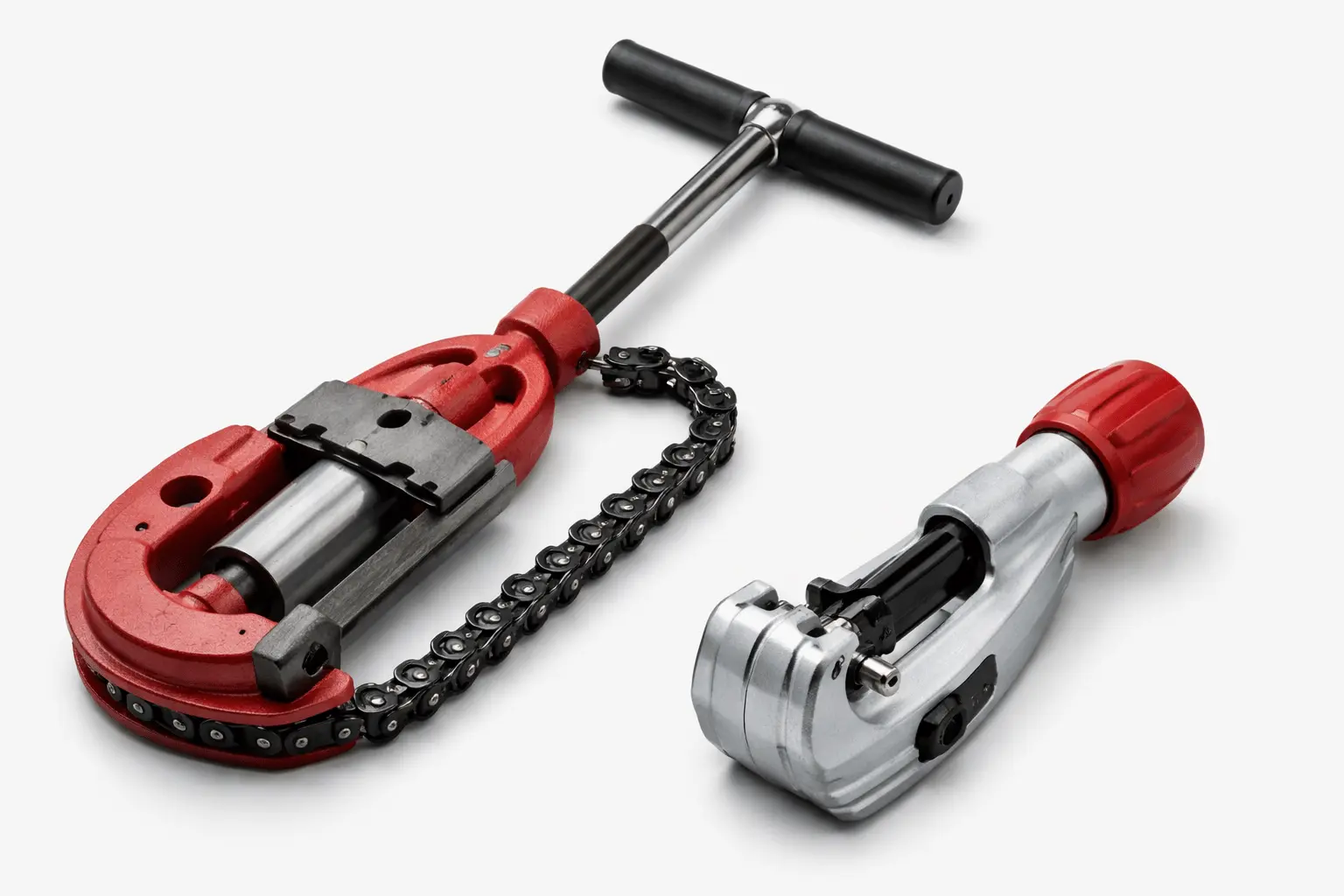

The design of each cutting tool reflects the properties and standards of the material it is intended to cut.
Pipe Cutter
Pipe cutters are designed for materials used in fluid transport systems.
Typical characteristics include:
- Built to accommodate nominal pipe sizes and varying schedules
- Robust construction for cutting thicker walls
- Optimized for durability rather than fine dimensional accuracy
- Commonly used in plumbing, installation, and pipeline work
Tube Cutter
Tube cutters are designed for precision-sized materials.
Typical characteristics include:
- Designed for exact outside diameters and wall thicknesses
- Optimized for clean, accurate cuts
- Reduced risk of material deformation
- Commonly used in manufacturing and fabrication environments
Why Using the Wrong Cutter Causes Problems
Using the incorrect cutter can compromise both the material and the final assembly.
- Using a pipe cutter on thin-walled tubing can deform the tube and affect fitment
- Using a tube cutter on thick-walled pipes may result in inefficient cutting or tool damage
Selecting the correct cutter ensures material integrity, clean cuts, and efficient workflow.
How to Choose the Right Cutter
Step 1: Identify the Material Type
- Materials labeled by NPS and Schedule are pipes
- Materials labeled by exact OD and wall thickness are tubes
Step 2: Understand Outside Diameter Compatibility
For pipes, the outside diameter remains constant for a given NPS, allowing the same fittings to be used across different schedules.
For tubes, exact OD matching is essential for precise assemblies.
Step 3: Consider the Application
- Plumbing, drainage, gas, and fluid systems typically require pipe cutters
- Structural, mechanical, and fabrication applications require tube cutters
Step 4: Specify Dimensions Clearly
- Always specify both NPS and Schedule when ordering pipes
- Always specify exact OD and wall thickness when ordering tubes
Clear specification prevents ordering mistakes, installation issues, and tool mismatch.
Conclusion: The Right Tool Follows the Right Standard
The difference between a pipe cutter and a tube cutter is defined by industrial standards, not terminology.
Pipes use nominal sizing to ensure system compatibility in fluid transport applications. Tubes use exact dimensions to meet precision and structural requirements.
Understanding this distinction ensures correct tool selection, protects material integrity, and improves overall efficiency in professional applications.