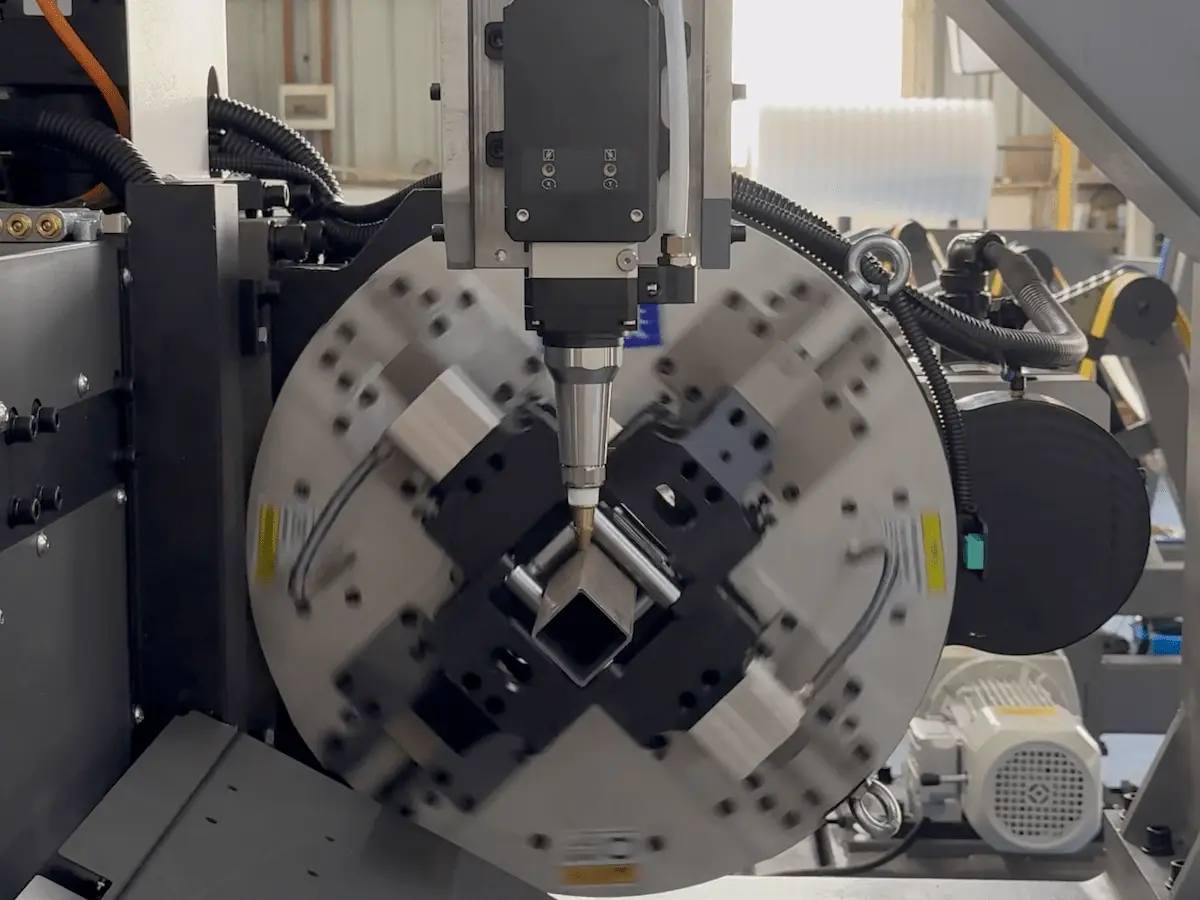
Il taglio laser di un tubo comporta il fissaggio del tubo in una macchina per il taglio laser di tubi, centrandolo automaticamente, impostando i parametri di taglio e utilizzando un raggio laser focalizzato per tagliare il tubo con precisione lungo un percorso programmato.
Il processo combina il controllo CNC, il movimento rotativo e la tecnologia laser per ottenere tagli precisi e privi di bave su tubi e condotti metallici.
Che cos’è il taglio laser dei tubi?
Il taglio laser dei tubi è un processo che utilizza un raggio laser focalizzato per tagliare, asolare, forare o sagomare tubi e condotti metallici. A differenza del taglio della lamiera piana, il taglio laser dei tubi richiede:
- Bloccaggio e rotazione accurati del tubo
- Centraggio automatico per compensare la deformazione del tubo
- Sincronizzazione precisa degli assi lineari e rotativi
Una macchina per il taglio laser dei tubi può lavorare tubi tondi, quadrati, rettangolari e profili di forme speciali con elevata ripetibilità e sprechi di materiale minimi.
1. Preparazione prima del taglio laser di un tubo
Proper preparation is critical for safety, accuracy, and cutting quality.
Check the Work Area
-
Ensure the working area is clean and free of obstacles
- Confirm all safety guards and protective covers are in place
Inspect the Machine
- Check the laser source, chiller water temperature, and gas pressure
- Inspect the cutting nozzle and focusing lens for contamination or damage
- Confirm all electrical and pneumatic connections are normal
Prepare Materials and Tools
- Verify tube material, diameter, thickness, and length
- Prepare drawings or cutting programs in advance
2. Power-On and Machine Startup
Correct startup order protects the machine and ensures stable operation.
Standard Startup Sequence
- Main power switch
- Voltage stabilizer
- Emergency stop reset
- CNC control system
- Servo system
- Water chiller
- Laser source

Once the control system finishes initialization, perform a homing operation to reset all axes to their reference positions
3. Drawing and Programming for Tube Laser Cutting
Create or Import Tube Cutting Drawings

Using professional tube cutting software (such as TubesT):
- Draw parts directly or import existing CAD files
-
Define tube type (round, square, rectangular, etc.)
- Enter tube dimensions and wall thickness

Process and Nesting Setup
- Define cutting paths, pierce points, and lead-ins
- Apply cutting technology parameters
- Perform automatic nesting to optimize material usage
Export the completed task as a cutting program for the machine.
4. Machine Calibration and Debugging
Before cutting, accurate calibration is essential.
Capacitive Calibration
With the tube clamped in the chuck:
- Perform nozzle capacitance calibration
- Ensure stable height control during cutting
B-Axis and Chuck Calibration
- Calibrate the B-axis center
- Check chuck clamping force and support alignment
- Ensure smooth tube rotation without slipping
5. Loading and Centering the Tube
Tube Loading
- Load tubes manually or using an automatic loading system
- Clamp the tube securely with the chuck
Automatic Centering
- Run the automatic tube centering function
- The system detects tube deformation and calculates offset values
- This ensures the laser cutting head stays aligned with the tube center
Accurate centering is a key advantage of modern tube laser cutting machines and directly affects cutting precision.
6. Set Laser Cutting Parameters
Laser cutting parameters must be adjusted according to material and thickness.
Key Parameters Include:
- Cutting speed (m/min)
- Nozzle height (mm)
- Assist gas type (air, oxygen, nitrogen)
- Gas pressure (BAR)
- Peak power (%)
- Duty cycle (%)
- Focus position (mm)

Tip for beginners: Always start with recommended parameters and perform a short test cut before mass production
7. Start the Laser Tube Cutting Process
Trial Cutting
- Click the “Start” button to begin cutting
- Perform a short test cut
- Check edge quality, burrs, and dimensional accuracy
Batch Production
Once the result is confirmed:
- Enable cycle processing mode
- Set production quantity and interval time
- Monitor the cutting process in real time
During cutting, observe:
- Stability of cutting sparks
- Smooth removal of scrap
- Gas pressure and machine status
8. Unloading and Shutdown
After cutting is completed:
Unloading
- Use the unloading system to remove finished parts
- Avoid direct contact with hot materials
Shutdown Procedure
- Turn off the laser source
- Close assist gas valves
- Power down the machine in the correct sequence
- Clean residual scrap from the work area
Safety Tips for Laser Tube Cutting
- Never place hands or body parts inside the protected cutting area
- Press the emergency stop immediately in case of abnormal conditions
- Do not modify parameters without proper training
- Contact technical support if issues cannot be resolved
Final Thoughts
Comprendere come tagliare correttamente un tubo con il laser è fondamentale per ottenere elevata precisione, qualità stabile ed efficienza produttiva. Seguendo un processo standardizzato di taglio laser dei tubi e utilizzando una macchina per il taglio laser dei tubi affidabile, i produttori possono ridurre in modo significativo i costi di manodopera e migliorare la produttività complessiva.
Le moderne macchine per il taglio dei tubi con laser a fibra rendono possibile la lavorazione di forme di tubi complesse con velocità e costanza, rendendole uno strumento indispensabile nell’industria odierna della lavorazione dei metalli.