1. What is H-Beam?

Definition of H-Beam
H-Beam, also known as I-beam, W-beam (wide flange), or universal beam, is a structural beam made of rolled steel. The H-beam is named due to its distinctive H-shaped cross-section, which provides excellent strength and rigidity.
H-beams are widely used in various applications, including:
- Construction of tall buildings and skyscrapers
- Bridge construction
- Industrial structures and warehouses
- Heavy machinery frames
- Foundation support for large structures (as H-piles)
- Trailers and truck beds
2. What is an H-Beam Laser Cutting Machine?
Definition
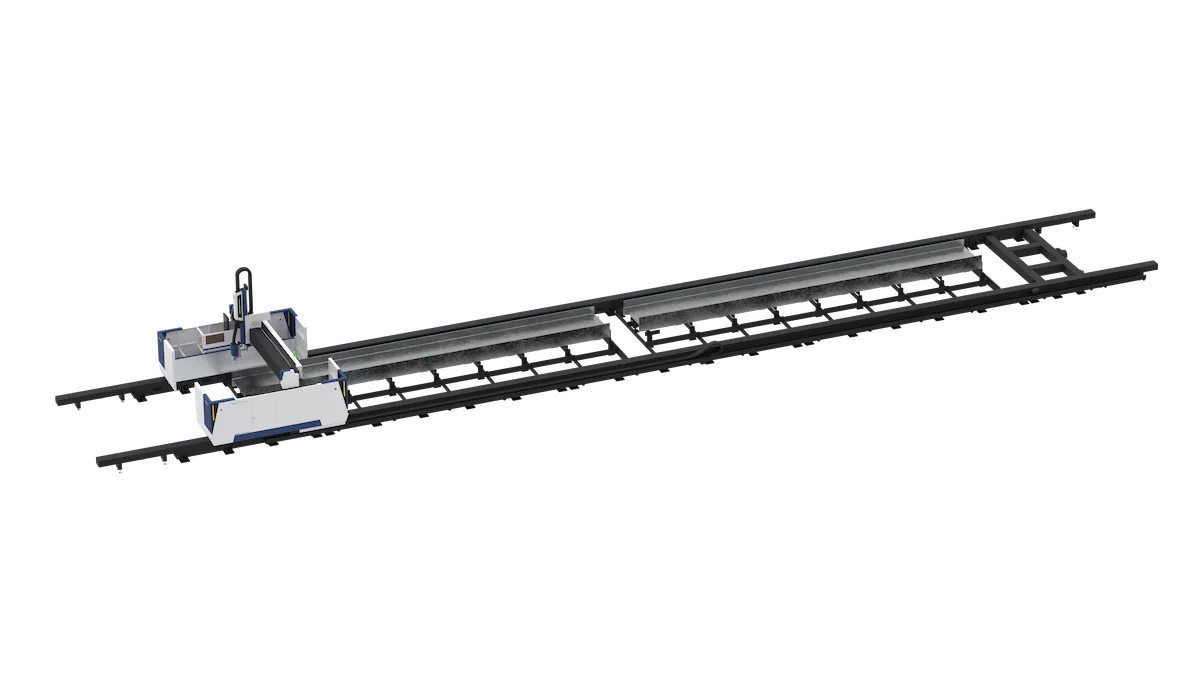
An H-beam laser cutting machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to cut and process H-beams using laser technology. These machines provide precise cuts and can handle the complex shapes and sizes of H-beams. It can replace tedious processes such as marking, drilling, manual multi-pass transfer, manual bevel cutting, manual grinding, etc., and can realize H-beam beveling, cutting, hole cutting, marking processing, and rootless cutting of welding holes or lock holes. It can also be combined with assembled welding equipment to form an automatic steel processing line, reducing costs and increasing efficiency for enterprises.
Functions of H-Beam Laser Cutting Machine
- Cutting: Precise cutting of H-beams into various lengths and shapes.
- Drilling: Creating holes and slots in the H-beams for assembly purposes.
- Marking: Laser marking for identification and alignment during construction.
- Bevel Cutting: Cutting at various angles to prepare the beams for welding and assembly.
Composition of H-Beam Laser Cutting Machine
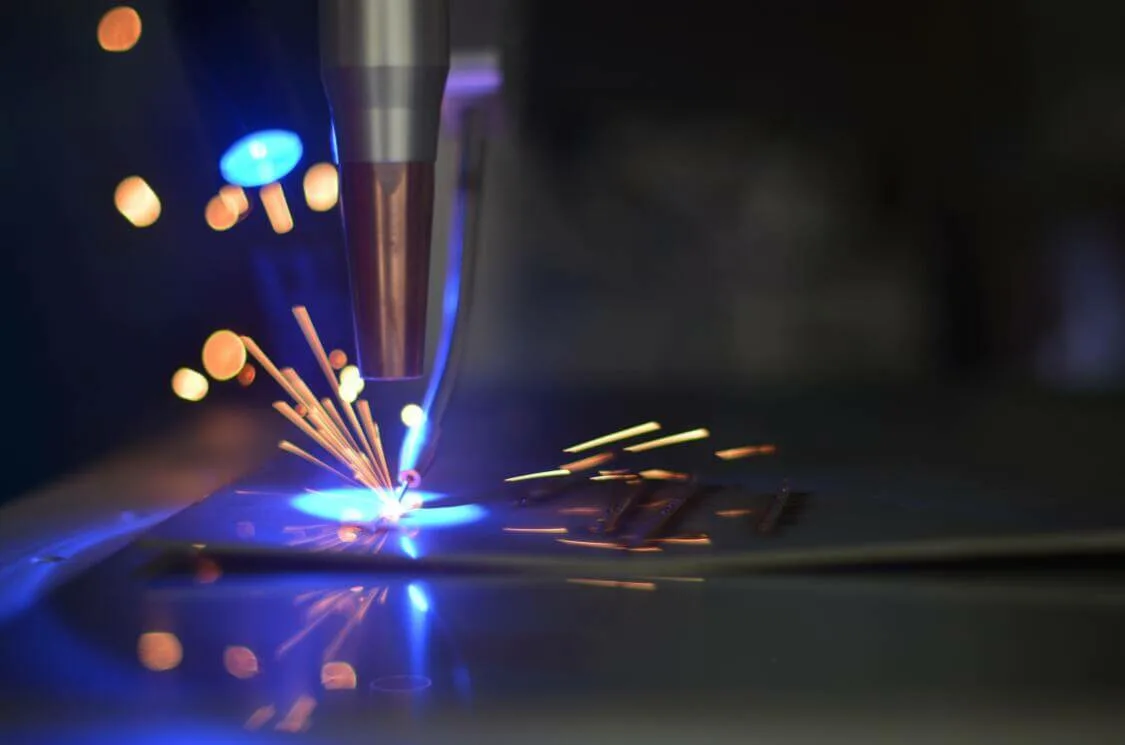
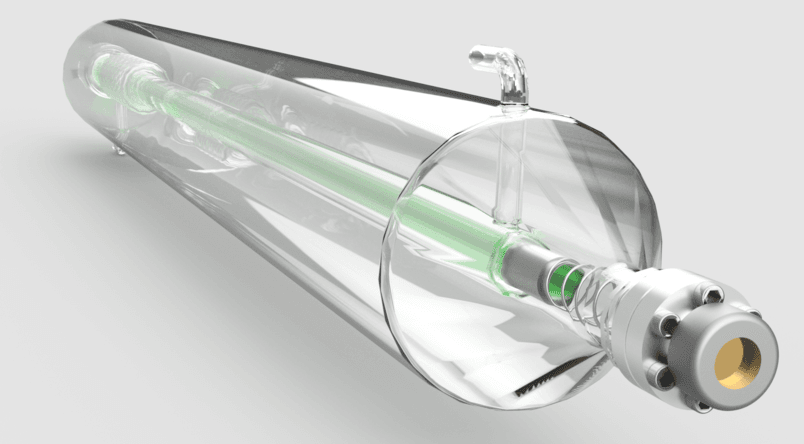
- Laser Source: Generates the laser beam used for cutting.
- Cutting Head: Directs the laser beam onto the H-beam.
- CNC System: Controls the cutting process and ensures precision.
- Cooling System: Maintains the optimal temperature of the machine components.
- Support and Feeding Mechanism: Holds and moves the H-beam during the cutting process.
Applicable Industries:
- Construction and steel fabrication
- Shipbuilding
- Automotive manufacturing
- Industrial equipment production
- Infrastructure development
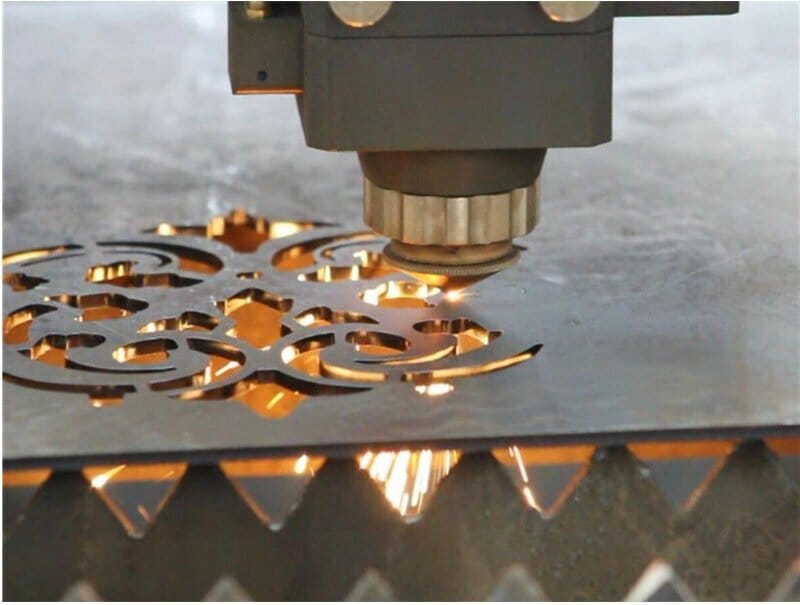
3. Why Use Laser to Cut H-Beam?
Advantages of H-Beam Laser Cutting
- High precision and accuracy in cutting complex shapes
- Faster processing speeds compared to traditional methods
- Minimal material waste and narrow kerf width
- No tool wear, as it’s a non-contact process
- Ability to cut various thicknesses and materials
- Reduced post-processing requirements
- Improved edge quality and reduced heat-affected zone
Disadvantages of H-Beam Laser
- High initial investment costs
- Energy-intensive process
- Limitations on maximum material thickness
- Potential for harmful fumes and gases, requiring proper ventilation
- Specialized operator training required
4. How to Correctly Choose an H-Beam Laser Cutting Machine?
When choosing an H-beam laser cutting machine, consider the following factors:
1. Machine Parameters Based on Workpiece Size and Weight:
- Determine the maximum H-beam dimensions (height, width, and length) you need to process
- Consider the weight capacity of the machine’s material handling system
- Ensure the working envelope of the machine can accommodate your largest workpieces
2. Laser Power Selection:
- Higher power (6-12 kW) for thicker materials and faster cutting speeds
- Lower power (2-4 kW) for thinner materials and more intricate cutting
3. Single or Double-Station Configuration:
- Single-station for smaller operations or limited space
- Double-station for increased productivity, allowing loading/unloading while cutting
4. Automatic Loading and Unloading:
- Consider automated material handling for improved efficiency and reduced labor costs
- Evaluate the space requirements and integration with existing workflows
5. Bevel Cutting Functionality:
- Determine if your applications require bevel cuts for weld preparation
- Assess the maximum bevel angle and thickness capabilities
Additional Considerations:
- Software compatibility and ease of use
- Service and support availability
- Safety features and certifications
- Future scalability and upgrade options
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select an H-beam laser cutting machine that best suits your production needs, budget, and long-term business goals. Remember to consult with machine manufacturers and industry experts to ensure you make an informed decision based on your specific requirements.