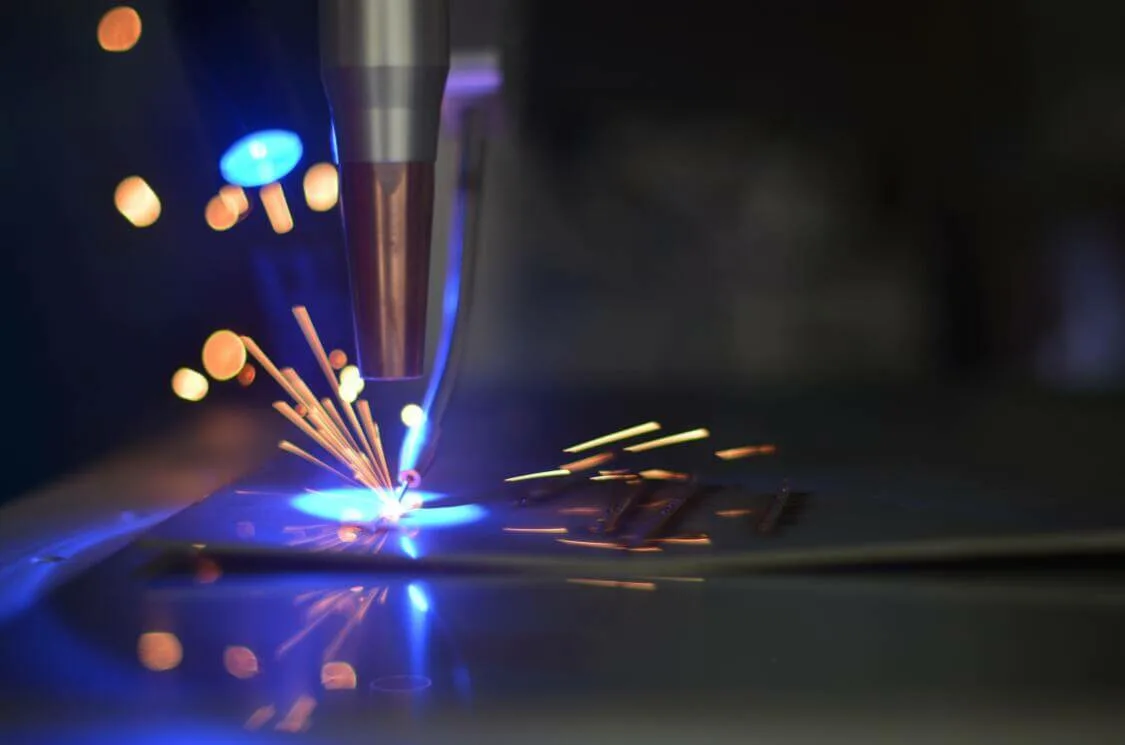
Laser cutting technologies have revolutionized manufacturing and design, offering precision and flexibility for various applications. This article explores the differences between 2D and 3D laser cutting, guiding engineers, designers, and fabricators in choosing the right method for their projects.
Understanding 2D Laser Cutting

정의 프로세스
2D 레이저 절단,또한 알려져 있으로 평판을 절단,가 매우 초점을 맞춘 레이저 광속을 잘라 평면 재료과 같은 강철,스테인리스 스틸,알루미늄,비철금속을 정밀.
프로세스를 포함하는 레이저 공명기를 만드는 광선 감독으로 절단 머리에 초점을 맞추고,을 통해 렌즈를 녹여,화상,또는 증발 물질이다.
일반적으로,이러한 기계 세 축:두 위치 중 하나는 Z 축을 조정하는 절단 머리의 거리에서는 제품.
응용 프로그램과 자료
2D 레이저 절단하는 중요한 기업을 위해 요구하는 정밀 절단에서 얇은 금속판. 그것은 널리 사용되는 재료와 같이 가벼운 강철,스테인리스 스틸,알루미늄,구리,놋쇠,두께에 이르기까지 0.8mm30mm.
그 응용 프로그램을 확장하는 산업 제조,학교,기업,그리고 취미입니다.
장점 및 단점
장점:
- 높은 정밀도와 품질을 인하의 정확도+/-0.1mm.
- 빠른 처리 속도를 줄이고,수작업 및 운영 비용을 절감합니다.
- Minimal thermal distortion, ensuring clean cuts and reducing post-processing needs.
단점:
- Limited to cutting materials up to 25 mm in thickness.
- High energy consumption and significant initial equipment costs.
- Requires adequate ventilation due to harmful gases and fumes produced during cutting.
Understanding 3D Laser Cutting
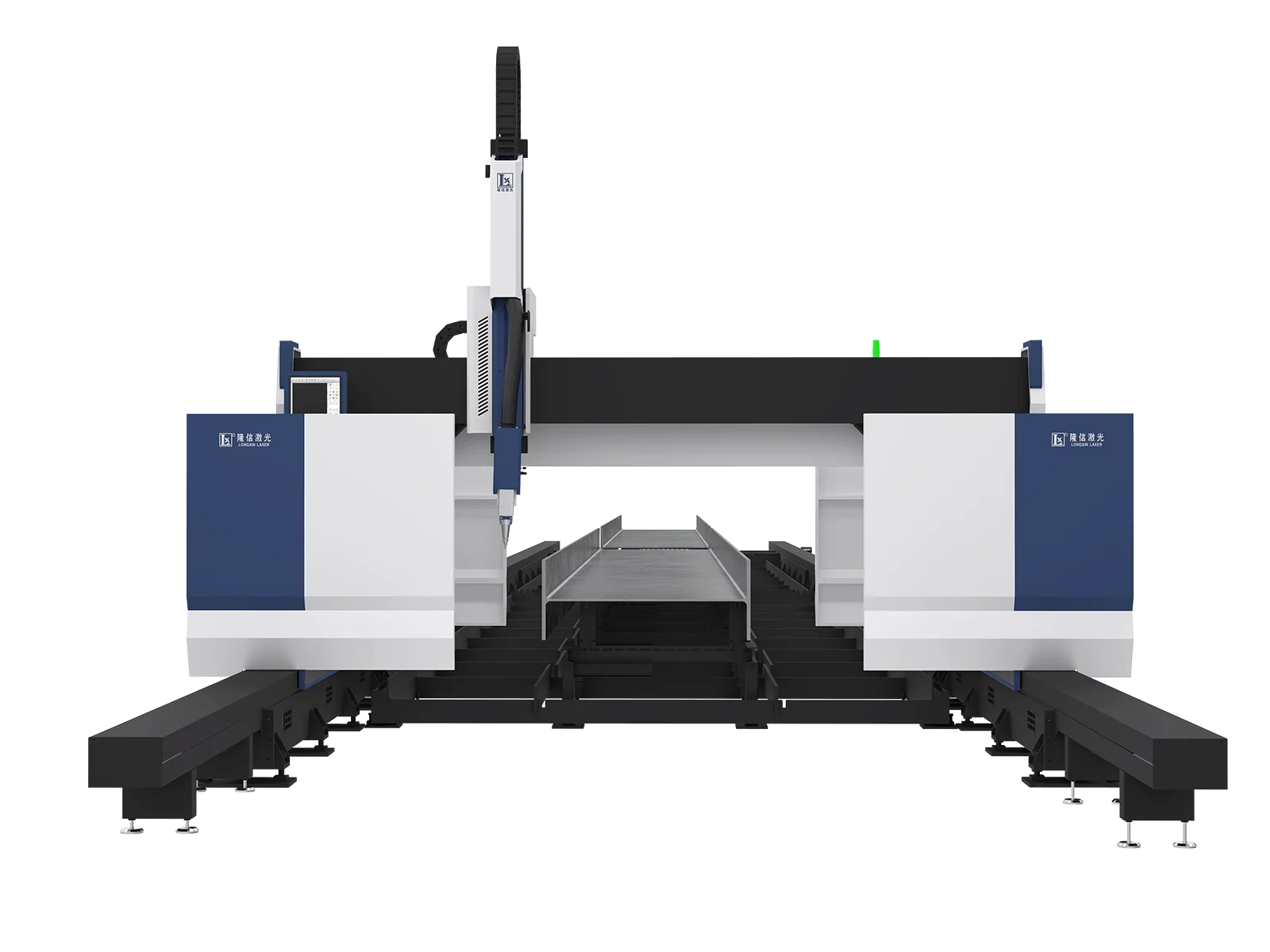
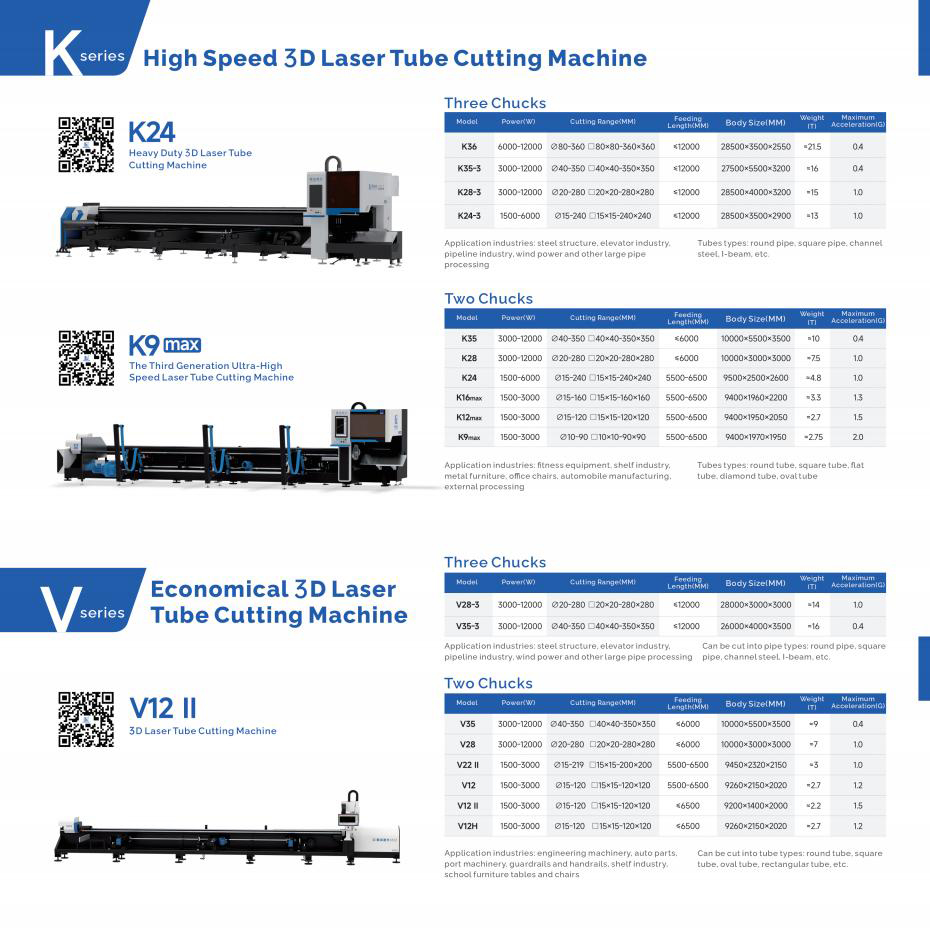
정의 프로세스
3D laser cutting uses a focused laser beam directed by a complex system moving along multiple axes, allowing intricate cuts on various material surfaces.
This method involves a rotary head that adjusts to the contours of the material, maintaining optimal distance and angle for precise cutting.
응용 프로그램과 자료
3D laser cutting is particularly advantageous for industries requiring high precision for complex parts, such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
It can cut metals like stainless steel and aluminum, as well as other industrial materials, to create custom shapes and designs up to 20 mm thick.
장점 및 단점
장점:
- High efficiency and speed, surpassing traditional cutting methods.
- 정밀 절단을 최소화 열 영향을 받는 지역 및 적은 재료의 낭비이다.
- Versatility in handling various material profiles and thicknesses.
단점:
- High initial investment and power consumption.
- Intensive maintenance requirements, particularly for certain lasers like CO2.
- Safety concerns due to hazardous fumes necessitating proper ventilation.
Key Differences Between 2D and 3D Laser Cutting
| Aspect | 2D Laser Cutting | 3D 레이저 절단 |
|---|---|---|
| Capability | Cuts flat, two-dimensional shapes | Cuts intricate, three-dimensional shapes |
| 정밀도 | High precision on flat materials | High precision across multiple axes |
| Material Handling | Limited to flat, consistent thickness materials | Handles various shapes, sizes, and thicknesses |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, suitable for simpler projects | Higher initial investment, suitable for complex projects |
| Applications | Signage, metal components, parts manufacturing | Aerospace, automotive, electronics, medical equipment, architecture |
결론
Understanding the differences between 2D and 3D laser cutting technologies is essential for making informed decisions in manufacturing and design. While 2D laser cutting offers simplicity, precision, and cost-effectiveness for flat materials, 3D laser cutting provides unmatched flexibility for intricate three-dimensional shapes and complex geometries.
Selecting the appropriate technology ensures optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and innovation in your projects, pushing the boundaries of what’s achievable in modern manufacturing.